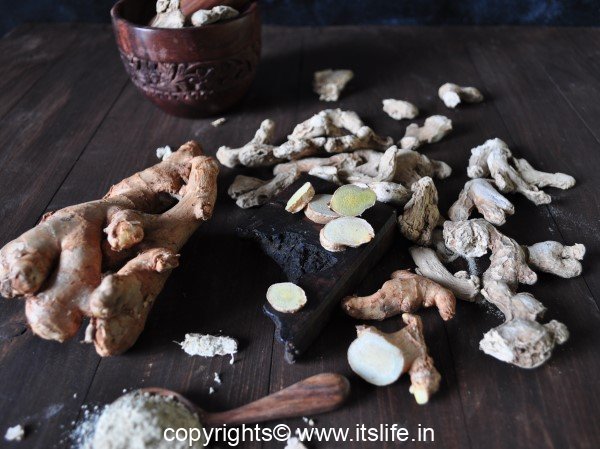
You cannot think of Indian Cuisine without Ginger. Ginger is an integral part of Indian cooking, which enhances the taste and aroma of the dish.
In Kannada Ginger is known as Shunti, Alla, in Hindi it is known as Adrak, Inji in Malayalam and Tamil, Sunth in Sanskrit. Botanical name is Zingiber officinale and belongs to Zingiberaceae (Ginger) family. Ginger was first cultivated in Asia and is grown in India, Southeast Asia, West Africa and the Caribbean. India is the largest producer of Ginger.
The Ginger is an herbaceous perennial plant with upright stems and narrow leaves, which are arranged in a pair on each stem. The plant grows from a tuber like rhizome to a height of 4 feet. The leaves are green and about 3/4th inch wide and 7 inches long.
The inflorescence grows on a separate shoot rising from the rhizome and forms a dense spike. The spike can be up to 3 inches tall. The flowers are yellow green with purple lips and has cream-colored blotches on them. The bracts are green with translucent margins.
Ginger is grown for the edible rhizome. It is used in many cuisines for its flavor. Dry Ginger powder is also used to enhance the taste of many dishes.
Ginger is used in traditional medicines like Ayurveda and Chinese medicines. Dry Ginger leaves are used to weave mats.
Propagation:
Ginger plant can be grown from Rhizomes. The Ginger is harvested when the stalk shrivels. Ginger grows well in warm, humid environment, and in well-drained soils.
Recipes using Ginger: