The other common name of Rubber Tree are Para Rubber Tree, Sharinga Tree, Seringueira. The botanical name is Hevea brasiliensis and belongs to Euphorbiaceae (Castor) family. Rubber tree is native of Amazon rain forests. As this is an economically important tree, it is now grown in other parts of South America, South-East Asia, and Africa.
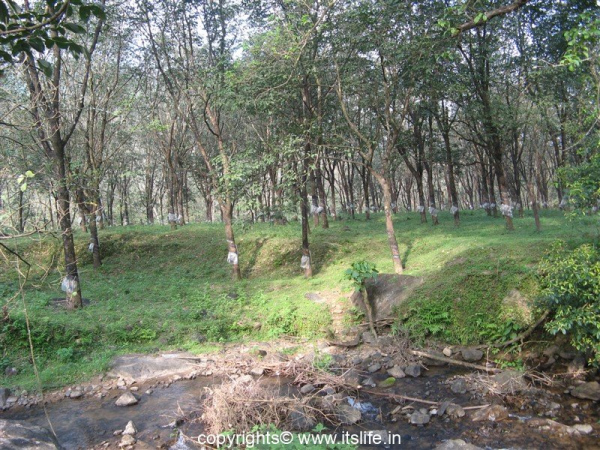
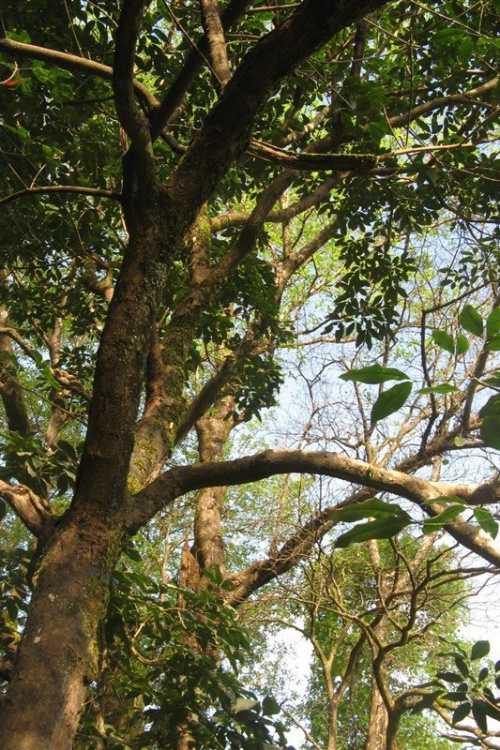
The Rubber tree is a deciduous tree and grows to a height of 30 to 40 meters.
The trunk is brown and cylindrical and has a smooth surface.
The trunk produces cream-colored latex.
Extracting latex affects the height of the tree. Latex is the primary source of natural rubber.
The leaves are green and grow in spirals with three leaflets. The small flowers have a strong smell. They are pale yellow and do not have petals. The fruit is a three-lobed capsule.
Uses:
The bark is tapped for the milky white latex. Incisions are made on the bark of the tree ensuring that the tree is not harmed. The latex is the raw material used to manufacture rubber. The process of collecting the white latex from the rubber tree is known as Rubber tapping.
Once the latex production decreased, the trees are cut, and the wood is used to make furniture.
Propagation:
Rubber trees are propagated using seeds. You can also propagate using graft budding. Rubber trees need tropical climate with annual rainfall of 2000 – 4500 mm. Minimum and maximum temperature should be ranged from 25 to 34°C with 80 % relative humidity is ideal for cultivation. Regions prone to heavy winds should be avoided.